INDICATORS
Jumping Those Hurdles
The Chartmill Value Indicator
by Dirk Vandycke
Oscillators identify overvalued and undervalued situations. They have their advantages, especially in short-term valuations, but also struggle with recurring disadvantages. In this, the first of a series, we will look at how to overcome these disadvantages.
Any technical analyst is familiar with the concept of an oscillator. Oscillators like relative strength index (RSI), moving average convergence/divergence (MACD), and stochastic try to capture a relative short-term valuation of their underlying series. Almost all classical oscillators fall into two categories. On the one hand, there are range compression oscillators like RSI, which basically try to squeeze a price chart into a fixed range like [0, 100] or [-1, +1]. Smoothing oscillators like MACD, on the other hand, use moving averages to get rid of noise. Neither set of these classic oscillators interprets the relative value of a stock, which accounts for almost all of their shortcomings.
HOW DO YOU COPE?
Not only that, range compression oscillators just give you the same information you see if you squint at the original price chart. They also have a stickiness problem, which is the tendency to stick to the minimum or maximum of their interval during strong trends, as they try to fit trends of any length into the same narrow range. Those trends almost always get compressed in the small oversold or overbought zones. That is because the biggest part of their range is reserved for short-term reactions to price. This gives extended overbought or oversold signals with the trend just marching on, making those signals useless. Smoothing oscillators on their part have the same lagging problems as moving averages, the primary components on which they are built.
To make things even worse, they all need parameters, which leaves them open to a lot of subjectivity in their usage and interpretation. This puts traders who are backtesting these oscillators in harm’s way, as they might fall victim to curve-fitting. This lack of transparency can be seen in the numerous ways they are used, while in fact they are often nothing more than a small, distorted version of the original price chart.
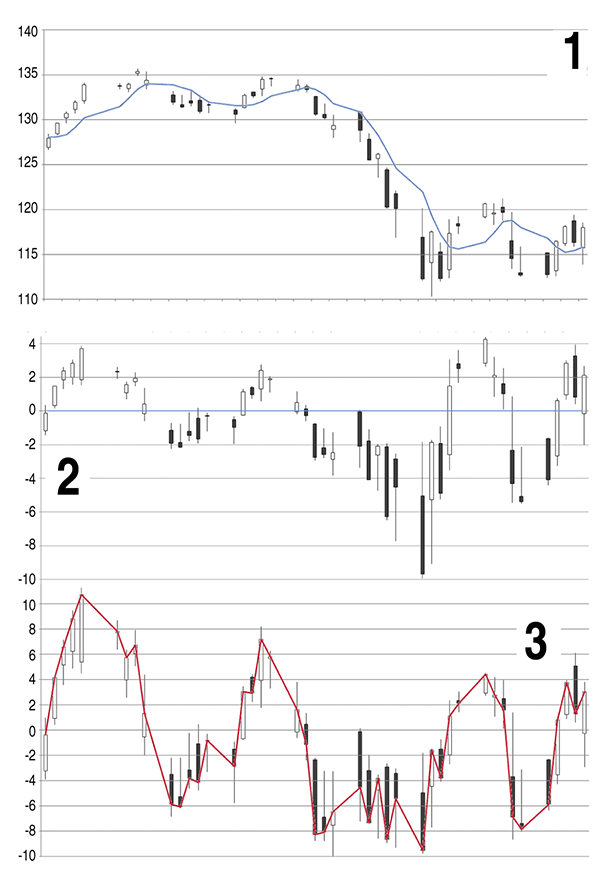
FIGURE 1: CONSTRUCTION OF CHARTMILL VALUE INDICATOR (CVI). The Chartmill value indicator is derived by statistical standardization. The consensus (median) line meandering through the original candles (1) is leveled to a straight line (2), with each candle keeping its relative distance to this line. In the final step (3), all data points are divided by a short-term volatility measure. The close of the normalized candles results in the CVI.
Excerpted from an article originally published in the January
2013 issue of Technical Analysis of Stocks & Commodities magazine. All rights reserved. © Copyright 2012, Technical Analysis, Inc.
Return to Contents
